Page Contents
Python WSGI Apps with LSAPI
LiteSpeed SAPI is the easiest and fastest way to run web applications with OpenLiteSpeed Web Server. OpenLiteSpeed supports LSAPI for Python applications through WSGI. WSGI (Web Server Gateway Interface) is a low-level interface between web servers and web applications. It allows Python applications designed for WSGI to be used in a variety of settings. It is important to note that, while most Python applications are WSGI-compatible, not all are.
This wiki will go over how to set up OLS to run Python applications with LWSGI. This wiki assumes that you already have a working version of Python installed and virtual hosts set up to run it on.
- Initial Setup
- Verify WSGI Script
- Django Setup
- Set up Django with a Virtual Environment
- Verify Django
- Set up Flask with a Virtual Environment
- Verify Flask
- Optional Settings
Requirements
- OpenLiteSpeed version 1.4.42+
Initial Setup
Install Python3 Library
If you haven’t already, please install the Python3 dev package (note that it must be Python 3.5 or higher):
CentOS
yum install python3-devel
yum install python3-pipYou may need to use:
yum install python36-devel
yum install python36-pipUbuntu
apt install build-essential
apt-get install python3-devInstall WSGI
The easiest and fastest way to run web applications with LiteSpeed Web Server is to install and compile wsgi-lsapi.
For python2 user, please use e.g. python, python2.7 to compile. You should get the latest version. Get the Python LSAPI version here. Replace the VERSION below with the version number you find there (like 2.1).
curl -O http://www.litespeedtech.com/packages/lsapi/wsgi-lsapi-VERSION.tgz
tar xf wsgi-lsapi-VERSION.tgz
cd wsgi-lsapi-VERSION
python3 ./configure.py
make
cp lswsgi /usr/local/lsws/fcgi-bin/Note. Python2 and python3 compile can not be used together.
How to Verify WSGI Script
Set up Context
This example assumes you are using the default document root + URI: /python/
Navigate to Web Admin > Virtual Hosts > Context > Add
- Type =
App Server - URI =
/python/ - Location =
/usr/local/lsws/Example/python/ - Binary Path =
/usr/local/lsws/fcgi-bin/lswsgi - Application Type =
WSGI
Note that the URI is not used to find the default initial script. It always uses wsgi.py or whatever file name is specified in the Startup File configuration value.
Create wsgi.py script
Create a python directory under your document root.
Then, create a wsgi.py file with the following content:
import os
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(__file__))
def application(environ, start_response):
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/plain')])
message = 'It works!\n'
version = 'Python %s\n' % sys.version.split()[0]
response = '\n'.join([message, version])
return [response.encode()]Verification
Visit http://Server_IP:Port/python/ in your browser and you should see:
It works!
Python x.x.xDjango Setup
Create Project
If you haven’t installed Django, please do so through pip3
pip3 install djangoCreate demo project under the /var/www/html/ folder.
Create the folder if it doesn’t exist.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/cd /var/www/html/
django-admin startproject demoDjango Settings
Edit settings.py inside the inner folder (may be demo/demo) to allow hosts
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*'] The STATICFILES_DIRS tells Django where to look for static files that are not tied to a particular app. In this case, we just told Django to also look for static files in a folder called static in our root folder, not just in our apps.
STATIC_URL = '/python/static/'
STATIC_ROOT = '/var/www/html/demo/public/static'- Note 1:
/python/static/depends on your context settings - Note 2: putting the
staticfolder underpublicis required
Collect static files in the directory where manage.py exists (may be one level up)
mkdir -p public/static
python3 manage.py collectstaticCreate admin super user
python3 manage.py migrate
python3 manage.py createsuperuserChange owner
Centos:
chown -R nobody:nobody /var/www/html/demoUbuntu:
chown -R nobody:nogroup /var/www/html/demoThis example assumes you are using the default document root + URI: /python/
Navigate to Web Admin > Virtual Hosts > Context > Add
- Type =
App Server - URI =
/python/ - Location =
/var/www/html/demo/ - Binary Path =
/usr/local/lsws/fcgi-bin/lswsgi - Application Type =
WSGI - Startup File =
demo/wsgi.py
Set up Django with a Virtual Environment
Create Virtual Environment
Create the folder for the virtualenv django project if it doesn’t exist.
mkdir -p /var/www/html/Note. Putting the virtual environment outside of the web server config and document root folders is recommended.
Use the virtualenv tool to create the virtual environment.
virtualenv /var/www/html/Or specify python version and give the virtual environment access to the system site-packages dir
virtualenv -p python3 --system-site-packages /var/www/html/Access and Activate the virtual environment
source /var/www/html/bin/activateCheck if python loaded from virtual environment
which pythonCreate Project
pip and python already link to python version 3 in virtulenv, so if you haven’t installed Django, please try to install through pip,
pip install djangoCreate the demo project under /var/www/html/
cd /var/www/html/
django-admin startproject demoDjango Settings
Edit settings.py inside the inner folder to allow hosts
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']Edit settings.py inside the inner folder for managing static files
The STATICFILES_DIRS tells Django where to look for static files that are not tied to a particular app. In this case, we just told Django to also look for static files in a folder called static in our root folder, not just in our apps.
STATIC_ROOT = '/var/www/html/demo/public/static'- Note: putting the
staticfolder underpublicis required
Collect static files
mkdir -p public/static
python manage.py collectstaticCreate admin super user
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuserChange owner
chown -R nobody:nogroup /var/www/html/demoSet up Context
This example assumes you are using the default document root + URI: /
Navigate to Web Admin > Virtual Hosts > Context > Add
- Type =
App Server - URI =
/ - Location =
/var/www/html/demo/ - Binary Path =
/usr/local/lsws/fcgi-bin/lswsgi - Application Type =
WSGI - Startup File =
demo/wsgi.py - Environment =
PYTHONPATH=/var/www/html/lib/python3.8:/var/www/html/demo - Environment =
LS_PYTHONBIN=/var/www/html/bin/python
- Type =
Be sure to substitute the listed python version (python 3.8) with your current one.
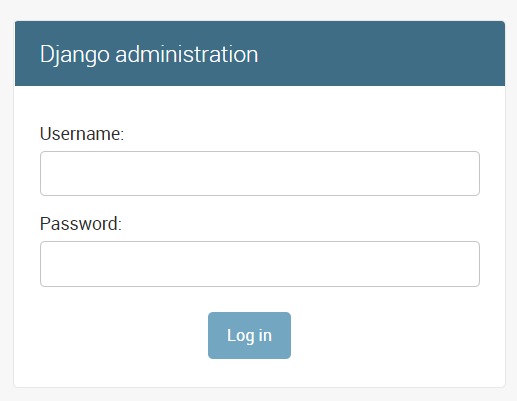
Verify Django
Visit http://Server_IP:Port/admin in your browser and you should see the admin page.
Set up Flask with a Virtual Environment
Create Virtual Environment
virtualenv venvOr (specify python version)
virtualenv -p python3 venvAccess and Activate the virtual environment
source venv/bin/activateCheck if python loaded from virtual environment
which pythonCreate Project
pip and python already link to python version 3 in virtulenv, so if you haven’t installed Flask, please try to install through pip,
pip3 install flaskCreate demo project under e.g. Virtual Host Root: /var/www/html/
mkdir /var/www/html/demo
cd /var/www/html/demoFlask example code
Let’s create a directory named app and then add the example code under it, naming the file __init__.py.
mkdir appvi /var/www/html/demo/app/__init__.py
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def hello():
return "Hello Flask!"Create a wsgi file in the project, and this file will add your python files to the python path.
vi /var/www/html/demo/wsgi.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, '/var/www/html/demo')
from app import app as applicationChange owner
chown -R nobody:nogroup /var/www/html/demoSet up Context
This example assumes you are using the default document root + URI: /
Navigate to Web Admin > Virtual Hosts > Context > Add
- Type =
App Server - URI =
/ - Location =
/var/www/html/demo/ - Binary Path =
/usr/local/lsws/fcgi-bin/lswsgi - Application Type =
WSGI - Startup File =
wsgi.py - Environment =
PYTHONPATH=/var/www/html/lib/python3.8:/var/www/html/demo - Environment =
LS_PYTHONBIN=/var/www/html/bin/python
- Type =
Be sure to substitute the listed python version (python3.8) with your current one.
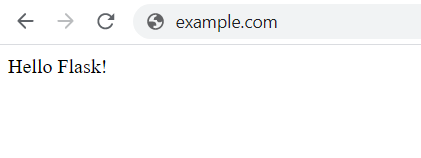
Verify Flask
Visit http://Server_IP/ in your browser and you should see Hello Flask!
Optional Settings
Custom Binary Path
If you want to change the LSWSGI path, just update the Context and set Binary Path = /usr/lswsgi.
Custom Startup File Name
If you want to change the default WSGI file name from passenger_wsgi.py to example_wsgi.py, just update the Context and set Startup File = example_wsgi.py.

